Last week, Vicente Vazquez, head of infrastructure at Colba Technologies, did a presentation for one of our customers.
And we want to share it with the community. I hope you enjoy it. And if you like. Share it :)
Terraform Cloud Main Features:
- Organization-based model where each organization or team can have their own workspace.
- Enables cross-workspace share of data
- Integration with version control systems: Github, Gitlabs, AzureDevops, bitbucket, in addition to VCS-triggered runs.
- Manges state remotely via API, UI, and CLI-based integration with Terraform Cloud
- Provide private modules in a private registry
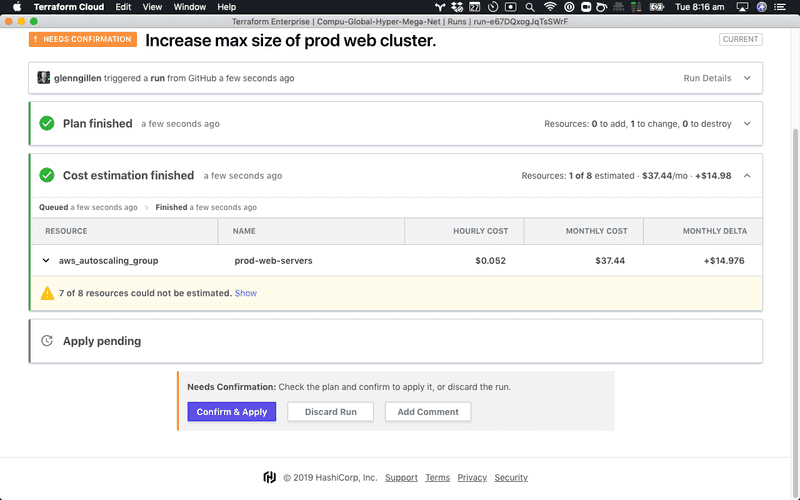
- [Paid Features] Cost estimation feature, which can look at your terraform plan output and estimate that cost of deployment.
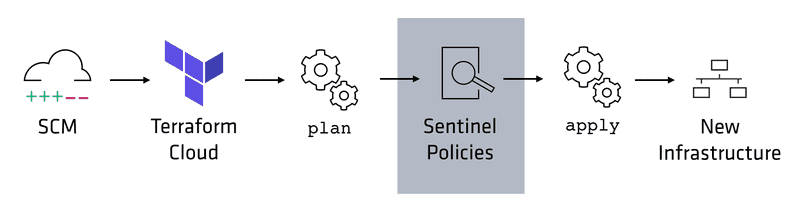
- [Paid Features] Sentinel for enforcing policies on your code before it is deployed
Benefits
- Workspaces are hosted in terraform cloud instead of your local system.
- Use Cloud Workspaces for distinct deployments . You don’t need to worry about segregation, storage or even security of your workspace
- All the state files are stored in Terraform´s managed cloud and can be shared between organizations.
- State files are versioned so it is possible to review state changes and compare it
- Terraform deployment execution and all related activity is recovered and that allows for auditing and investigating deployments more readily and easily
- You do not need to have a local CLI terminal with Terraform installed to kick off deployment with manual terraform apply.
- Hashicorp will execute your ‘plan’, ‘apply and ‘init’ commands on their own hosted and managed VMs in the HashiCorp cloud
- Private Module repository allows us to use versions
- It is possible to interact with workspaces using APIs.
Workspace OSS vs Cloud Workspaces
Terraform OSS Workspaces
Creates alternate state files against code in the same directory. So you can issue multiple, distinct deployments against the same code. It does that by creating a separate directory within the main terraform directory called the ‘terrafrom.tfstate.d’ directory where it houses a folder for each state file tracked by the different workspaces.
| Component | Local Terraform | Terraform Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Terraform configuration | On disk | In linked version control repository, or periodically uploaded via API/CLI |
| Variable values | As .tfvars files, as CLI arguments, or in shell environment | In workspace |
| State | On disk or in remote backend | In workspace |
| Credentials and secrets | In shell environment or entered at prompts | In workspace, stored as sensitive variables |
Terrafrom Cloud Execution Mode
We can work in 2 execution modes when we are using Terraform Cloud
Local: Your plans and applies occur on machines you control. Terraform Cloud is only used to store and synchronize state.
Remote: Your plans and applies occur on Terraform Cloud's infrastructure. You and your team have the ability to review and collaborate on runs within the app.
Private Module Repository
- Create based in repository content
- Version modules using tags
- Documentation of modules by version using README
After tag is created the module will be access using module block like this:
module "instance" {
source = "app.terraform.io/colba/instance/aws"
version = "1.0.0"
}
Cloud Variables
- Create variables for each workspace
- Variables can be defined as Sensitive
- Variables can be defined in HCL format
- Environment variables can be created to be injected into Terraform Hosted VMs
Terraform Workflows
Workflow Version control workflow
Most common Store your Terraform configuration in a git repository, and trigger runs based on pull requests and merges.
CLI-driven workflow
Trigger remote Terraform runs from your local command line.
API-driven workflow
A more advanced option. Integrate Terraform into a larger pipeline using the Terraform API.
Terraform cost estimation [Paid Features]
Terraform Sentinel [Paid Features]
Terraform Sentinel Policy example
# all EC2 instances have instance types from an allowed list
# Import common-functions/tfplan-functions/tfplan-functions.sentinel
# with alias "plan"
import "tfplan-functions" as plan
# Allowed EC2 Instance Types
# Include "null" to allow missing or computed values
allowed_types = ["t2.small", "t2.medium", "t2.large"]
# Get all EC2 instances
allEC2Instances = plan.find_resources("aws_instance")
# Filter to EC2 instances with violations
# Warnings will be printed for all violations since the last
# parameter is true
violatingEC2Instances = plan.filter_attribute_not_in_list(
allEC2Instances,
"instance_type",
allowed_types,
true)
# Count violations
violations = length(violatingEC2Instances["messages"])
# Main rule
main = rule {
violations is 0
}
Migrate our project to Terraform
Create simple project
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
The project can be use local backend or remote like S3
Login into terraform cloud
terraform login
Terraform will be request to use API key in this task.
Change current project Backend
We are using S3 Backend
terraform {
backend "s3" {
profile = "your-aws-profile"
bucket = "your-backed-name"
key = "terraform.tfstate"
region = "eu-central-1"
}
}
Migrationg from S3 to remote(Terraform cloud) Backend
terraform {
backend "remote" {
hostname = "app.terraform.io"
organization = "organization_name"
workspaces {
prefix = "client-"
}
}
}
Init first time Terraform Cloud
Check what happen when we try to init
terraform init
│ Error: Backend configuration changed
│
│ A change in the backend configuration has been detected,
| which may require migrating existing state.
│
│ If you wish to attempt automatic migration of the state,
| use "terraform init -migrate-state".
│ If you wish to store the current configuration with no
| changes to the state, use "terraform init -reconfigure".
terraform init -migrate-state
Terraform detected that the backend type changed from "s3"
to "remote".
The "remote" backend configuration only allows named
workspaces! Please provide a new workspace name
(e.g. dev, test) that will be used to migrate the existing
default workspace.
Enter a value: dev
After this step our worksapce called client-dev will be created into Terraform Cloud under our organization.